Plant Health Department
Plant Health Department

















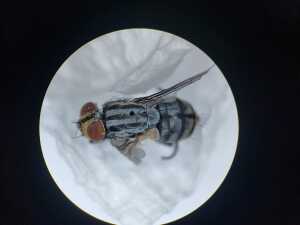

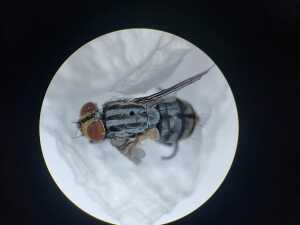
Overview
The Plant Health Department is responsible for implementing the functions of the National Plant Protection Organization. We safeguard agriculture, natural resources and the environment from the negative impacts of regulated pests and key endemic pests that can affect agricultural production, thereby contributing to food security, and gaining market access and trade opportunities for Belize.
Plant Health Priorities
Constitutes an integral component of the plant protection system and provides technical justification for decision making in support of the regulatory system for importations. It is the principal technical and scientific to determine restrictions of commodities of very high risk and to decide on the conditions for importation for proposed importations.
Import permits are issued with phytosanitary import conditions gathered on the basis of conclusions reached by using an appropriate pest risk analysis or evaluation of available scientific information. These permits are emitted with the intention of preventing the introduction of quarantine pests or limit the entry of regulated non-quarantine pests with imported commodities and other regulated articles.
Plant Health is responsible for maintaining a favorable phytosanitary status of the country. It is also the official point for notification of pest outbreaks. These activities are carried out through surveillance programmes, either active or passive and continuous or periodic.
The introduction of quarantine pests endanger our agricultural production systems through outbreaks that can reduce yields or devastate crops and natural ecosystems. Similarly, these can have a great impact on trade due to the imposition of new condition or sanctions and potential loss of export markets. The department is always vigilant and acts rapidly in cases of new outbreaks, to eradicate these pests or if not possible to maintain sound management programmes to reduce the impact of these.
One of the most successful programmes in this respect has been the maintenance of pest free status for the Mediterranean Fruitfly, a programm now spanning many decades. This has provided the opportunity for new industries such as the papaya and habanero pepper industries.
When quarantine pests are introduced and discovered promptly, the affected areas are delimited and checkpoints are established to prevent the mobilization of these pests to other free areas. This goes hand in hand with eradication programmes.
Strict control over certain planting material is maintained for established periods of time after entry, to observe any manifestation of systemic pests. This is done in collaboration with the relevant industries as a measure to safeguard the principal productive sectors of the country.
Plant Health investigates pest situations and outbreaks in the field either to evaluate the impact of these on crops or to corroborate if these are endemic pests or may be newly introduced pests. Producers are advised on management options to minimize losses.
Plant Health personnel identify pests to verify field samples, samples submitted from surveillance programmes, and samples of interceptions from the points of entry submitted by the Quarantine Department. In cases when the capacity for identification of certain pests is not available in-house, the department sends samples to reference laboratories in the region for final diagnosis.
One of the most successful programmes in this respect has been the maintenance of pest free status for the Mediterranean Fruitfly, a programme now spanning many decades. This has provided the opportunity for new industries such as the papaya and habanero pepper industries.
FOC TR4 (Fusarium oxysporium f.sp. cubense TR4)
Rugose Spiraling Whitefly (Aleurodicus rugioperculatus)
Description: This whitefly is larger than many other whitefly species and is known for the characteristic spiraling pattern of its eggs on leaves. Adult whiteflies are white with a waxy coating.
Symptoms: Infestation leads to heavy sooty mold due to honeydew excreted by the whiteflies, yellowing of leaves, and general plant stress. The presence of spiraling egg patterns on the undersides of leaves is a key indicator.
Control:
- Biological: Natural predators such as lady beetles, lacewings, and parasitoid wasps.
- Chemical: Horticultural oils and insecticidal soaps can be effective.
- Cultural: Regular monitoring and removing infested leaves can help control the population.
Affected Plants: Coconut palms, banana plants, avocado trees, and various ornamental plants.
Chinch Bug (Blissus spp.)
- Description: Small, black and white insects, approximately 1/5 inch long. Nymphs are red with a white band across their back.
- Symptoms: Irregular patches of dead grass that enlarge over time. Grass turns yellow and then brown, often resembling drought stress.
- Control:
- Biological: Beneficial nematodes and insect predators like big-eyed bugs.
- Chemical: Insecticides specifically labeled for chinch bug control.
- Cultural: Maintaining healthy turf through proper watering and fertilization can reduce susceptibility.
- Affected Plants: Primarily turfgrass such as St. Augustinegrass, zoysiagrass, and bermudagrass.
Northern Corn Leaf Blight (Exserohilum turcicum)
- Description: Fungal disease characterized by long, elliptical grayish-green lesions on corn leaves.
- Symptoms: Lesions are cigar-shaped and can become quite large. Severe infections cause premature leaf death, reducing photosynthesis and yield.
- Control:
- Cultural: Crop rotation and resistant hybrids can reduce the incidence.
- Chemical: Fungicides can be applied, especially in areas with a history of severe outbreaks.
- Biological: No significant biological control methods currently available.
- Affected Plants: Primarily affects corn (maize).
Coconut Leaf Spot Disease (Pestaliopsis palmarun)
- Description: Disease caused by the fungus Pestalotiopsis palmarum, leading to characteristic spots on coconut leaves.
- Symptoms: Small, yellow to brown spots with grayish centers. Spots can merge, causing large necrotic areas, leading to leaf drop.
- Control:
- Cultural: Removing and destroying infected leaves, improving air circulation by proper spacing, and avoiding overhead irrigation.
- Chemical: Fungicides can be applied as a preventive measure in severely affected areas.
- Biological: No significant biological control methods currently available.
- Affected Plants: Primarily affects coconut palms, but can also infect other palm species.
Aphids (Aphidoidea)
- Description: Small, soft-bodied insects, usually green but can be yellow, black, or brown.
- Symptoms: Yellowing leaves, distorted growth, sticky honeydew on leaves.
- Control: Insecticidal soap, neem oil, introducing natural predators like ladybugs.
- Affected Plants: Roses, tomatoes, peppers, lettuce, beans, and many ornamental plants.
Spider Mites (Tetranychidae)
- Description: Tiny, spider-like mites, often red or yellow.
- Symptoms: Fine webbing on plants, stippled or yellow leaves.
- Control: Miticides, horticultural oil, maintaining high humidity.
- Affected Plants: Tomatoes, strawberries, houseplants, and various ornamental plants.
Whiteflies (Aleyrodidae)
- Description: Small, white, moth-like insects.
- Symptoms: Yellowing or silvering of leaves, sticky honeydew, sooty mold.
- Control: Yellow sticky traps, insecticidal soap, beneficial insects like Encarsia formosa.
- Affected Plants: Tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, eggplants, and many houseplants.
Mealybugs (Pseudococcidae)
- Description: White, cottony masses on plants.
- Symptoms: Yellowing leaves, stunted growth, sticky honeydew.
- Control: Rubbing alcohol on a cotton swab, insecticidal soap, predatory insects like ladybugs.
- Affected Plants: Orchids, succulents, houseplants, and various fruit trees.
Scale Insects (Coccoidea)
- Description: Small, oval insects covered with a protective shell.
- Symptoms: Yellowing leaves, reduced vigor, sticky honeydew.
- Control: Pruning infested branches, horticultural oil, introducing parasitic wasps.
- Affected Plants: Citrus trees, camellias, ferns, and houseplants.
Thrips (Thysanoptera)
- Description: Tiny, slender insects, often yellow or black.
- Symptoms: Silvery or speckled leaves, distorted flowers.
- Control: Blue sticky traps, neem oil, beneficial insects like predatory mites.
- Affected Plants: Onions, beans, carrots, and various flowers like roses and gladioli.
Caterpillars (Lepidoptera larvae)
- Description: Larvae of butterflies and moths, various colors and patterns.
- Symptoms: Chewed leaves, holes in leaves, frass (caterpillar droppings).
- Control: Handpicking, Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), beneficial insects like parasitic wasps.
- Affected Plants: Cabbage, broccoli, tomatoes, fruit trees, and various flowers.
Leaf Miners
- Description: Larvae that live inside and eat leaf tissue, creating tunnels.
- Symptoms: White or brown trails in leaves.
- Control: Removing infested leaves, neem oil, introducing parasitic wasps.
- Affected Plants: Spinach, chard, beets, and various ornamentals.
Japanese Beetles (Popillia japonica)
- Description: Metallic green and bronze beetles.
- Symptoms: Skeletonized leaves, flowers and fruit damage.
- Control: Handpicking, neem oil, introducing beneficial nematodes.
- Affected Plants: Roses, grapes, raspberries, and various ornamental trees.
Slugs and Snails (Gastropoda)
- Description: Soft-bodied mollusks with or without shells.
- Symptoms: Irregular holes in leaves, slime trails.
- Control: Beer traps, iron phosphate baits, diatomaceous earth.
- Affected Plants: Hostas, lettuce, strawberries, and various seedlings.

Plant Health Application Forms
Import Conditions: Ensuring Safe and Healthy Plant Trade
Import conditions are essential requirements that govern the entry of plants, plant products and other regulated articles into Belize. These conditions are put in place to protect agriculture, our natural ecosystems, from the introduction of harmful pests. Import conditions are necessary for anyone involved in the trade or purchase of plant materials, as well as for the farming community and general public that benefit from a secure and healthy agricultural system.
What Are Import Conditions?
Import conditions are the set of science-based rules and standards issued by BAHA, that must be met for plants, plant products and other regulated articles to be legally imported into Belize. These conditions ensure that imported items do not carry regulated pests, or other harmful organisms that could pose a threat to our agriculture and ecosystems.For stakeholders and the general public, understanding import conditions highlights the importance of plant health in global trade and encourages informed and responsible choices. By supporting and complying with these regulations, everyone can contribute to a healthier, more secure agricultural system in Belize.
Key Components of Import Conditions
- Phytosanitary Certificates:
- Verification of Health: Importing plants and plant products into Belize may require a phytosanitary certificate issued by the exporting country’s plant health authority. This certificate verifies that the plants or plant products have been inspected and are free from specific regulated pests.
- Compliance Documentation: The certificate accompanies the shipment and is checked by BAHA’s quarantine authorities at Belize’s points of entry, to ensure compliance with import conditions.
- Valid Import Permit:
- Import Permit: must not exceed ten items i.e. ten species or varieties, or ten plant products from a single origin. Different origins require separate permits even for the same commodity.
- Pre-Import Inspections:
- Export Country Inspections: Before shipment, plants and plant products are inspected in the exporting country to identify and mitigate any pest risks.
- Import Country Inspections: Upon arrival, additional inspections and testing may be conducted by BAHA’s quarantine authorities to ensure compliance with local regulations.
- Quarantine Measures:
- Detention and Isolation of imported consignments: Some imports may be subject to quarantine upon arrival, where they are isolated and monitored for a specific period to ensure they are free of regulated pests.
- Treatment Requirements: Import conditions may require specific treatments such as fumigation, heat treatment, or pesticide application to eliminate any potential regulated pests.
- Non-compliant consignments may be destroyed if determined to be of high risk or if a treatment is not feasible.
- Non-compliant consignments may be returned to origin at the expense of the importer.
- Prohibited and Restricted Items:
- Prohibited Species: Certain plants and plant products may be completely prohibited from entry if they pose a high risk of introducing regulated pests.
- Restricted Imports: Some commodities may be subject to restrictions or special conditions, such as only being allowed from certain countries or regions known to be free of specific pests, or having to meet certain strict pre-export conditions and treatments.
- Post-Entry Monitoring:
- Follow-Up Inspections: Some imported plants may be subject to follow-up inspections and monitoring after their initial entry to ensure no regulated pests have escaped detection.
Benefits to the General Public
- Protection of Our Local Agriculture:
- Preventing Pests: Import conditions help prevent the introduction of regulated pests that could devastate local agriculture, natural forested areas, ecosystems , and also ensuring stable food production and supply.
- Safeguarding Biodiversity: By controlling the import of potentially harmful species, these regulations help protect the biodiversity of local ecosystems.
- Economic Stability:
- Reducing Economic Losses: Preventing pest outbreaks reduces the economic losses that farmers and the agricultural industries might otherwise face.
- Supporting Trade: By maintaining a healthy agricultural environment and a clean phytosanitary status, the country can maintain market access for our major commodities and improve foreign exchange.
- Public Health:
- Safe Food Supply: Ensuring that imported plant products are free from pests contributes to a safe and reliable food supply for consumers.
- Environmental Health: Protecting plants and preventing the entry of invasive species also helps maintain natural ecosystems, clean air, water, and soil, contributing to overall environmental well-being.
- Consumer Confidence:
- Quality Assurance: Knowing that imported plants and plant products meet stringent health standards boosts consumer confidence in the quality and safety of these products.
How the General Public Can Benefit
- Stay Informed:
- Awareness of Regulations: By understanding import conditions, consumers, farmers, agricultural industries and gardeners can make informed choices about the plants and plant products they purchase and import.
- Knowledge of Risks: Awareness of the risks associated with importing plants helps the relevant stakeholders and the public appreciate the importance of these regulations.
- Support Compliance:
- Buy Certified Products: Always opt for plant products that have been legally imported and comply with import conditions and carry the necessary certifications.
- Report Suspicious Items: Notify BAHA authorities if you encounter plant products that do not appear to meet import standards or if you observe any unusual plant health issues.
- Advocate for Strong Policies:
- Promote Plant Health: Support policies and initiatives that strengthen plant health regulations and promote safe trade practices.
- Community Education: Educate others about the importance of import conditions and the role they play in protecting local agriculture and ecosystems.
Export Certifications: Ensuring Safe and Healthy Plant Trade
Export certification plays a vital role in international trade by ensuring that plants and plant products meet the health standards of importing countries. This process helps prevent the spread of regulated pests, and protecting global agriculture and natural ecosystems. For the productive sector and export logistics services understanding export certifications can provide insights into the importance of plant health in international commerce and the measures taken to maintain it.
What is Export Certifications?
Export certification refers to official procedures carried out by the Plant Health Department of BAHA, which include rigorous inspection and testing of commodities confirming that plants and plant products meet specific phytosanitary requirements as determined by the importing country. The Department issues phytosanitary certificates and other supporting documents that attest to compliance with such conditions. These certifications are crucial for facilitating the smooth and safe cross-border trade of agricultural products.
How Export Certifications Work
- Inspection and Testing:
- Field Inspections: Plants and plant products are inspected in the field or at production sites as well as in packing facilities to ensure they are free from regulated pests.
- Laboratory Testing: Samples may be taken for laboratory analysis to detect any pest infestations that are not visible to the naked eye.
- Compliance with International Standards:
- Phytosanitary Standards: Export certifications ensure compliance with international phytosanitary standards set by organizations such as the International Plant Protection Convention (IPPC).
- Country-Specific Phytosanitary Requirements: Each importing country may have specific plant health requirements, and the inspection and certification process ensures these are met.
- Issuance of Certificates:
- Phytosanitary Certificates: Once plants or plant products pass inspections and tests, a phytosanitary certificate is issued. This document verifies that the shipment complies with the importing country’s phytosanitary regulations
- Treatment Certificates: Some countries require separate treatment certificates for specific commodities other than those stated in the phytosanitary certificate. The department issues these separately..
- Documentation for Trade: These certificates are included in the documentation accompanying the shipment, ensuring transparency and compliance during customs inspections.
Benefits of Export Certifications
- Protecting Global Agriculture:
- Preventing Cross-Border Pest Spread: By ensuring that exported plants are free from regulated pests, export certification helps prevent the spread and introduction of harmful organisms that can devastate crops and natural ecosystems.
- Safeguarding Food Security: Healthy plants contribute to stable agricultural production, supporting food security worldwide.
- Facilitating International Trade:
- Market Access: Export certification enables producers to access international markets, boosting trade opportunities and economic growth.
- Building Trust: Export Certification builds trust between trading partners, ensuring that agricultural products meet the required phytosanitary standards.
- Supporting Local Economies:
- Economic Growth: Access to international markets allows farmers and exporters to expand their businesses, generate foreign exchange and contribute to local and national economic development.
- Job Creation: Increased trade opportunities can lead to job creation in the agricultural and related sectors.
- Consumer Confidence:
- Quality Assurance: For consumers, export certifications provide assurance that imported plant products are healthy and safe, maintaining confidence in the quality of food agricultural planting material and ornamental plants.
How the General Public Can Benefit
- Understanding the Process:
- By learning about export certification, the general public can appreciate the measures taken to ensure the safety and quality of the plants and plant products they consume.
- Supporting Local Agriculture:
- Awareness of export certification can encourage support for local farmers and producers who adhere to high phytosanitary standards, promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
- Making Informed Choices:
- Consumers can make informed choices by opting for products that have been certified, knowing that these products have met stringent phytosanitary standards.
- Advocating for Plant Health:
- Understanding the importance of plant health in global trade can inspire individuals to advocate for robust plant health regulations and practices in their communities and beyond.
Export certification is a key component of safe and healthy international plant trade. This ensures that plants and plant products meet stringent phytosanitary standards, and protecting global agriculture and ecosystems. For the general public, understanding export certifications highlights the importance of plant health and the rigorous processes in place to maintain it. This knowledge not only fosters appreciation for the quality and safety of imported plant products but also encourages support for sustainable agricultural practices and robust plant health regulations.
Pest Surveillance
Pest Surveillance: Protecting Plant Health for a Better Future




Pest surveillance is a proactive approach to safeguarding the health of plants in our agricultural production areas, gardensand natural environments. By regularly monitoring and collecting data, we can detect and address potential issues early, ensuring that our plants stay healthy and productive. This practice benefits everyone, from home gardeners to commercial farmers, by maintaining the beauty and productivity of our green spaces.
What is Pest Surveillance?
Pest Surveillance involves a process whereby information on pests is obtained through specific surveillance and general surveillance, with the objective of detecting regulated pests and other pests of importance in a timely manner to eradicate, suppress, and prevent the further spread of these within a region or throughout the country. in an effort to protect agriculture and natural environments
How Does Pest Surveillance Work?
Specific surveillance is an official process carried out by the Plant Health Department of BAHA alone or in collaboration with industry stakeholders. It includes the following aspects:
- Regular Monitoring:
- Routine Checks: Key industries and production areas are routinely checked by Plant Health Officers for specific pests of quarantine importance. These may include whole fields or sentinel plots in high-risk areas.
- Data Collection:
- Field Notes: Officers keep records and include these in a database for reporting purposes and as proof of the absence of key pests.
- Sample Collection: Plant Health Officers collect suspicious samples of organisms or plant tissue, and submit these to the laboratory for confirmation.
- Use of Technology:
- Specific forms: Field data is generally collected on specific forms designed for the agricultural crop and target pests, which are then submitted for data storage.
- Mobile Apps: Officers also utilize specific apps for recording information for appropriate data storage.
- Remote Tools: For larger areas, drones and satellite imagery can be used to monitor plant health and spot issues from above, followed by ground inspections to verify.
- Documentation:
- Record Keeping: All surveillance data is stored for reporting purposes and for proof that the country is free of certain quarantine pests or to notify of the presence of new pests.
Benefits
- Producers can enjoy market access for their products since the country is maintained free of
quarantine pests. - Government and regulators: specific surveillance provides the basis for quick detection and possible eradication of quarantine pests. On the very least, it is possible to prevent further spread to other production areas
General Surveillance
General Surveillance: Everybody can contribute to Plant Health
General surveillance is an important part of determining the pest status of the country. It involves the casual observation of plants in our surroundings. Unlike specific active surveillance, which involves systematic and scheduled inspections by the plant health authority, general surveillance relies on the National Plant Protection Organization obtaining and verifying information on pests from different sources other than specific surveys. These may include reports made by the public, gardeners, researchers, farmers, technicians, and from academia and scientific publications. This approach empowers individuals to contribute to the health of plants in their production areas, gardens, communities, and natural environments.




How Does General Surveillance Work?
- Casual Observation:
- Gardeners: Keen gardeners observe their plans almost on a daily basis. Oftentimes new pests appear in these settings; as you tend to your garden, casually observe your plants for any signs of distress, such as discoloration, wilting, unusual spots, or insect activity.
- Farmers: Farmers are always concerned with pests and a significant part of management is related to pest management. Farmers know when there is a new pest problem.
- Extension Offices: Extension personnel are more likely to observe pests due to their continuous visits to farms and interactions with farmers. They are also generally aware of the probability of new pest incursions and the importance of these.
- Foresters: Forrest rangers and specialists may detect specific pests in these natural areas. Please report any new observations to the Plant Health department.
- Researchers: agricultural specialists have a tendency to discover new organisms and quickly write scientific articles to publish in journals. Please verify first with the Plant Health Department for clearance. Severe damage can be done to our exporters if our trading partners find out through an unofficial source and halt trade of certain commodities.
- Community Members: When walking through parks, community gardens, or public green spaces, members of the public may note irregularities in plants and may be curious enough to call somebody.
- Reporting:
- Local Authorities: Everybody is encouraged to report any suspicious plant health issues to local agricultural extension services, or directly to the Plant Health Department.
- Education and Awareness:
- Stay Informed: Farmers and gardeners are encouraged to learn about common plant pests in your area so you can recognize symptoms
- Spread the Word: : Everyone is encouraged to educate your family, friends, and neighbors about the importance of observing and reporting plant health issues and likewise to promptly inform of suspicious organisms and symptoms in plants.
Benefits to the General Public
- Community Health:
- Healthy plants contribute to a healthier industries and the environment, providing cleaner air, shade, and aesthetic beauty. Your observations can help maintain these benefits for everyone.
- Early Detection:
- By reporting problems early, you help prevent the spread of pests, protecting not just your plants but those in your community as well.
- Cost Savings:
- Early intervention can save significant costs associated with treatments or replacing diseased plants.
- Educational Value:
- General surveillance offers a learning opportunity for people of all ages. It encourages a deeper understanding and appreciation of plant health and environmental stewardship.
- Community Engagement:
- Engaging in general surveillance fosters a sense of community and shared responsibility for the local environment.
How You Can Get Involved
- Observe Regularly:
- Make it a habit to observe the plants in your farm, garden and community spaces regularly. Simple actions like walking your dog or visiting a park can become opportunities for surveillance.
- Learn and Share:
- Equip yourself with knowledge about common plant health issues. Share your knowledge with others to increase community awareness and participation.
- Report Promptly:
- Don’t hesitate to report any unusual plant symptoms to local authorities or through online platforms. Early reports can make a big difference.
- Join Local Groups:
- Participate in local gardening clubs, community gardens, or environmental groups. These organizations often have systems in place for reporting and addressing plant health issues.
- Use Technology:
- Take advantage of gardening apps to increase your knowledge and to report issues to the Plant Health Department or to the extension services of the Ministry of Agriculture.
Field Investigation and Diagnostics





Field investigation and diagnostics are critical components of plant health management. These processes involve systematic approaches to identify, monitor, and accurately identify plant pests. Accurate diagnostics and timely intervention can prevent widespread crop damage, ensuring healthy growth and optimal yield.
Steps in Field Investigation
- Preliminary Assessment:
- Visual Inspection: Plant Health officers and specialists conduct an initial visits to identify visible symptoms such as discoloration, wilting, spots, or deformities or the actual presence of pests such as insects and mites.
- Historical Analysis: The officers gather information on previous crop health issues, weather conditions, soil quality, and farming practices.
- Sampling:
- Representative Sampling: The officers collect samples from different parts of the field, including affected and unaffected areas, to ensure comprehensive analysis.
- Sample Handling: The officers properly label and store samples to prevent contamination and degradation and to ensure chain of custody.
- Symptom Documentation:
- Photographic Records: The officers take clear photographs of symptoms, including close-ups and wide-angle shots, to document the extent and nature of the problem.
- Detailed Notes: The officers record observations on the type, severity, and distribution of the organisms, symptoms, as well as environmental conditions and any recent changes in cultivation practices.
Diagnostics Techniques
- Visual Diagnosis:
- Symptom Comparison: The officers compare observed symptoms with known disease profiles from reference guides or online databases
- Expert Consultation: The officers seek advice from plant health specialists such as plant pathologists and entomologists for uncertain cases.
Importance of Accurate Diagnostics
- Targeted Treatment:
- Implementing precise treatments based on accurate diagnostics reduces the unnecessary use of pesticides and fertilizers, promoting sustainable practices.
- Early Intervention:
- Early detection and diagnosis allow for timely intervention for implementing eradication or mitigation to minimize the economic impact of pests on crop yield and quality.
- Informed Decision-Making:
- Accurate diagnostics provide essential data for making informed decisions on crop management, improving overall plant health and productivity.
Field investigation and diagnostics are vital for effective plant health management. By combining visual inspections, laboratory analyses, and advanced technologies, farmers and agronomists can accurately diagnose plant health issues and implement targeted interventions. This comprehensive approach will not only enhances crop productivity but also promotes sustainable agricultural practices, ensuring long-term environmental and economic benefits.
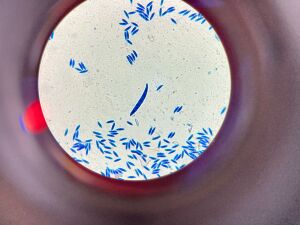
Laboratory Diagnostics




Laboratory diagnostics is a critical support process or making informed decisions and implementing effective pest management strategies. It also provides the Plant Health Department with the necessary basis for declaring the country or areas within the country as free of certain pests a condition creates market access and supports trade. Laboratory diagnosis also supports the import regulatory process by ensuring that regulated pests do not get introduced into the country through imported commodities.
Key Laboratory Diagnostic Techniques
- Microscopic Examination:
- Pest Identification: Microscopy allows for the detailed examination of plant tissues and organisms through the use of stereoscopes and compound microscopes to identify arthropod pests as well as pathogens such as fungi, bacteria, and nematodes.
- Molecular Diagnostics:
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): PCR is a highly sensitive technique used to detect specific DNA or RNA sequences of pathogens. This method allows for the rapid and accurate identification of viruses, bacteria, and fungi, even at low concentrations.
- Serological Tests:
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA): ELISA tests detect the presence of specific proteins or antigens associated with pathogens. This method is widely used for diagnosing viral infections in plants
- Culture Techniques:
- Pathogen Isolation: By culturing samples on selective media, lab technicians can isolate and identify pathogenic bacteria and fungi. This method is useful for confirming the presence of specific pathogens and for further testing their characteristics.
Benefits of Laboratory Diagnostics
- Accuracy and Precision:
- Laboratory diagnostics provide highly accurate and precise results, essential for identifying the exact cause of plant health issues which guide decision-making.
- Early Detection:
- Advanced techniques allow for the early detection of pathogens and nutrient imbalances, enabling timely intervention before problems become widespread.
- Informed Decision-Making:
- Detailed diagnostic information helps the Plant Health Department to initiate appropriate actions or to provide farmers and agronomists with the basis for make informed decisions about treatment strategies, and improving the effectiveness of plant health management.
- Cost-Effective Management:
- By accurately identifying the problem, laboratory diagnostics help avoid unnecessary treatments, reducing costs and minimizing environmental impact.
Trade Facilitation

Medfly Program

Pest Diagnostics

FOC TR4

How can the Plant Health Department help you?
Use the contact form below to contact us or check our FAQ to help assist you in your queries.
Plant pest is any species, strain or biotype of plant, animal or pathogenic agent injurious to plant or plant products. These may include plant species considered to be weeds, insects, mites and nematodes and pathogens such a fungi, bacteria, phytoplasmas, viruses and viroids.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a comprehensive approach to controlling pests and diseases that combines biological, cultural, mechanical, and chemical methods.
IPM aims to minimize environmental impact and promote sustainable pest control by using:
Biological Controls: : Natural predators or parasitoids, and entomopathogens
Cultural Practices: Crop rotation, proper planting times and resistant varieties
Mechanical Controls: Traps, barriers, hand-picking pests.
Chemical Controls: Targeted use of pesticides when necessary.
Common signs of nutrient deficiencies include:
Nitrogen: Yellowing of older leaves, stunted growth.
Phosphorus: Dark green or purplish leaves, poor root development.
Potassium: Brown or yellow leaf edges, weak stems.
Calcium: Tip burn on young leaves, blossom end rot in fruits.
A plant health diagnostic lab helps identify plant pests, and through various proven technicques such as microspcopy, molecular biology, microbiology and serology.
You can contribute by:
Reporting Issues: Inform BAHA or Ministry of Agricultural about unusual plant symptoms or pest outbreaks.
Practicing Good Hygiene: Clean tools and equipment to prevent the spread of diseases.
Educating Yourself: Learn about common plant health issues and best practices for prevention and control.
Supporting Research: Participate in citizen science projects and support organizations focused on plant health research and education.
Overview
Plant Health Department




















Overview
The Plant Health Department is responsible for implementing the functions of the National Plant Protection Organization. We safeguard agriculture, natural resources and the environment from the negative impacts of regulated pests and key endemic pests that can affect agricultural production, thereby contributing to food security, and gaining market access and trade opportunities for Belize.
What We Do/Who We Are
Plant Health Priorities
Constitutes an integral component of the plant protection system and provides technical justification for decision making in support of the regulatory system for importations. It is the principal technical and scientific to determine restrictions of commodities of very high risk and to decide on the conditions for importation for proposed importations.
Import permits are issued with phytosanitary import conditions gathered on the basis of conclusions reached by using an appropriate pest risk analysis or evaluation of available scientific information. These permits are emitted with the intention of preventing the introduction of quarantine pests or limit the entry of regulated non-quarantine pests with imported commodities and other regulated articles.
Plant Health is responsible for maintaining a favorable phytosanitary status of the country. It is also the official point for notification of pest outbreaks. These activities are carried out through surveillance programmes, either active or passive and continuous or periodic.
The introduction of quarantine pests endanger our agricultural production systems through outbreaks that can reduce yields or devastate crops and natural ecosystems. Similarly, these can have a great impact on trade due to the imposition of new condition or sanctions and potential loss of export markets. The department is always vigilant and acts rapidly in cases of new outbreaks, to eradicate these pests or if not possible to maintain sound management programmes to reduce the impact of these.
One of the most successful programmes in this respect has been the maintenance of pest free status for the Mediterranean Fruitfly, a programm now spanning many decades. This has provided the opportunity for new industries such as the papaya and habanero pepper industries.
When quarantine pests are introduced and discovered promptly, the affected areas are delimited and checkpoints are established to prevent the mobilization of these pests to other free areas. This goes hand in hand with eradication programmes.
Strict control over certain planting material is maintained for established periods of time after entry, to observe any manifestation of systemic pests. This is done in collaboration with the relevant industries as a measure to safeguard the principal productive sectors of the country.
Plant Health investigates pest situations and outbreaks in the field either to evaluate the impact of these on crops or to corroborate if these are endemic pests or may be newly introduced pests. Producers are advised on management options to minimize losses.
Plant Health personnel identify pests to verify field samples, samples submitted from surveillance programmes, and samples of interceptions from the points of entry submitted by the Quarantine Department. In cases when the capacity for identification of certain pests is not available in-house, the department sends samples to reference laboratories in the region for final diagnosis.
One of the most successful programmes in this respect has been the maintenance of pest free status for the Mediterranean Fruitfly, a programme now spanning many decades. This has provided the opportunity for new industries such as the papaya and habanero pepper industries.
Pest Information
FOC TR4 (Fusarium oxysporium f.sp. cubense TR4)
Rugose Spiraling Whitefly (Aleurodicus rugioperculatus)
Description: This whitefly is larger than many other whitefly species and is known for the characteristic spiraling pattern of its eggs on leaves. Adult whiteflies are white with a waxy coating.
Symptoms: Infestation leads to heavy sooty mold due to honeydew excreted by the whiteflies, yellowing of leaves, and general plant stress. The presence of spiraling egg patterns on the undersides of leaves is a key indicator.
Control:
- Biological: Natural predators such as lady beetles, lacewings, and parasitoid wasps.
- Chemical: Horticultural oils and insecticidal soaps can be effective.
- Cultural: Regular monitoring and removing infested leaves can help control the population.
Affected Plants: Coconut palms, banana plants, avocado trees, and various ornamental plants.
Chinch Bug (Blissus spp.)
- Description: Small, black and white insects, approximately 1/5 inch long. Nymphs are red with a white band across their back.
- Symptoms: Irregular patches of dead grass that enlarge over time. Grass turns yellow and then brown, often resembling drought stress.
- Control:
- Biological: Beneficial nematodes and insect predators like big-eyed bugs.
- Chemical: Insecticides specifically labeled for chinch bug control.
- Cultural: Maintaining healthy turf through proper watering and fertilization can reduce susceptibility.
- Affected Plants: Primarily turfgrass such as St. Augustinegrass, zoysiagrass, and bermudagrass.
Northern Corn Leaf Blight (Exserohilum turcicum)
- Description: Fungal disease characterized by long, elliptical grayish-green lesions on corn leaves.
- Symptoms: Lesions are cigar-shaped and can become quite large. Severe infections cause premature leaf death, reducing photosynthesis and yield.
- Control:
- Cultural: Crop rotation and resistant hybrids can reduce the incidence.
- Chemical: Fungicides can be applied, especially in areas with a history of severe outbreaks.
- Biological: No significant biological control methods currently available.
- Affected Plants: Primarily affects corn (maize).
Coconut Leaf Spot Disease (Pestaliopsis palmarun)
- Description: Disease caused by the fungus Pestalotiopsis palmarum, leading to characteristic spots on coconut leaves.
- Symptoms: Small, yellow to brown spots with grayish centers. Spots can merge, causing large necrotic areas, leading to leaf drop.
- Control:
- Cultural: Removing and destroying infected leaves, improving air circulation by proper spacing, and avoiding overhead irrigation.
- Chemical: Fungicides can be applied as a preventive measure in severely affected areas.
- Biological: No significant biological control methods currently available.
- Affected Plants: Primarily affects coconut palms, but can also infect other palm species.
Aphids (Aphidoidea)
- Description: Small, soft-bodied insects, usually green but can be yellow, black, or brown.
- Symptoms: Yellowing leaves, distorted growth, sticky honeydew on leaves.
- Control: Insecticidal soap, neem oil, introducing natural predators like ladybugs.
- Affected Plants: Roses, tomatoes, peppers, lettuce, beans, and many ornamental plants.
Spider Mites (Tetranychidae)
- Description: Tiny, spider-like mites, often red or yellow.
- Symptoms: Fine webbing on plants, stippled or yellow leaves.
- Control: Miticides, horticultural oil, maintaining high humidity.
- Affected Plants: Tomatoes, strawberries, houseplants, and various ornamental plants.
Whiteflies (Aleyrodidae)
- Description: Small, white, moth-like insects.
- Symptoms: Yellowing or silvering of leaves, sticky honeydew, sooty mold.
- Control: Yellow sticky traps, insecticidal soap, beneficial insects like Encarsia formosa.
- Affected Plants: Tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, eggplants, and many houseplants.
Mealybugs (Pseudococcidae)
- Description: White, cottony masses on plants.
- Symptoms: Yellowing leaves, stunted growth, sticky honeydew.
- Control: Rubbing alcohol on a cotton swab, insecticidal soap, predatory insects like ladybugs.
- Affected Plants: Orchids, succulents, houseplants, and various fruit trees.
Scale Insects (Coccoidea)
- Description: Small, oval insects covered with a protective shell.
- Symptoms: Yellowing leaves, reduced vigor, sticky honeydew.
- Control: Pruning infested branches, horticultural oil, introducing parasitic wasps.
- Affected Plants: Citrus trees, camellias, ferns, and houseplants.
Thrips (Thysanoptera)
- Description: Tiny, slender insects, often yellow or black.
- Symptoms: Silvery or speckled leaves, distorted flowers.
- Control: Blue sticky traps, neem oil, beneficial insects like predatory mites.
- Affected Plants: Onions, beans, carrots, and various flowers like roses and gladioli.
Caterpillars (Lepidoptera larvae)
- Description: Larvae of butterflies and moths, various colors and patterns.
- Symptoms: Chewed leaves, holes in leaves, frass (caterpillar droppings).
- Control: Handpicking, Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), beneficial insects like parasitic wasps.
- Affected Plants: Cabbage, broccoli, tomatoes, fruit trees, and various flowers.
Leaf Miners
- Description: Larvae that live inside and eat leaf tissue, creating tunnels.
- Symptoms: White or brown trails in leaves.
- Control: Removing infested leaves, neem oil, introducing parasitic wasps.
- Affected Plants: Spinach, chard, beets, and various ornamentals.
Japanese Beetles (Popillia japonica)
- Description: Metallic green and bronze beetles.
- Symptoms: Skeletonized leaves, flowers and fruit damage.
- Control: Handpicking, neem oil, introducing beneficial nematodes.
- Affected Plants: Roses, grapes, raspberries, and various ornamental trees.
Slugs and Snails (Gastropoda)
- Description: Soft-bodied mollusks with or without shells.
- Symptoms: Irregular holes in leaves, slime trails.
- Control: Beer traps, iron phosphate baits, diatomaceous earth.
- Affected Plants: Hostas, lettuce, strawberries, and various seedlings.
Medfly Program

Application Forms
Plant Health Application Forms
Import Conditions
Import Conditions: Ensuring Safe and Healthy Plant Trade
Import conditions are essential requirements that govern the entry of plants, plant products and other regulated articles into Belize. These conditions are put in place to protect agriculture, our natural ecosystems, from the introduction of harmful pests. Import conditions are necessary for anyone involved in the trade or purchase of plant materials, as well as for the farming community and general public that benefit from a secure and healthy agricultural system.
What Are Import Conditions?
Import conditions are the set of science-based rules and standards issued by BAHA, that must be met for plants, plant products and other regulated articles to be legally imported into Belize. These conditions ensure that imported items do not carry regulated pests, or other harmful organisms that could pose a threat to our agriculture and ecosystems.For stakeholders and the general public, understanding import conditions highlights the importance of plant health in global trade and encourages informed and responsible choices. By supporting and complying with these regulations, everyone can contribute to a healthier, more secure agricultural system in Belize.
Key Components of Import Conditions
- Phytosanitary Certificates:
- Verification of Health: Importing plants and plant products into Belize may require a phytosanitary certificate issued by the exporting country’s plant health authority. This certificate verifies that the plants or plant products have been inspected and are free from specific regulated pests.
- Compliance Documentation: The certificate accompanies the shipment and is checked by BAHA’s quarantine authorities at Belize’s points of entry, to ensure compliance with import conditions.
- Valid Import Permit:
- Import Permit: must not exceed ten items i.e. ten species or varieties, or ten plant products from a single origin. Different origins require separate permits even for the same commodity.
- Pre-Import Inspections:
- Export Country Inspections: Before shipment, plants and plant products are inspected in the exporting country to identify and mitigate any pest risks.
- Import Country Inspections: Upon arrival, additional inspections and testing may be conducted by BAHA’s quarantine authorities to ensure compliance with local regulations.
- Quarantine Measures:
- Detention and Isolation of imported consignments: Some imports may be subject to quarantine upon arrival, where they are isolated and monitored for a specific period to ensure they are free of regulated pests.
- Treatment Requirements: Import conditions may require specific treatments such as fumigation, heat treatment, or pesticide application to eliminate any potential regulated pests.
- Non-compliant consignments may be destroyed if determined to be of high risk or if a treatment is not feasible.
- Non-compliant consignments may be returned to origin at the expense of the importer.
- Prohibited and Restricted Items:
- Prohibited Species: Certain plants and plant products may be completely prohibited from entry if they pose a high risk of introducing regulated pests.
- Restricted Imports: Some commodities may be subject to restrictions or special conditions, such as only being allowed from certain countries or regions known to be free of specific pests, or having to meet certain strict pre-export conditions and treatments.
- Post-Entry Monitoring:
- Follow-Up Inspections: Some imported plants may be subject to follow-up inspections and monitoring after their initial entry to ensure no regulated pests have escaped detection.
Benefits to the General Public
- Protection of Our Local Agriculture:
- Preventing Pests: Import conditions help prevent the introduction of regulated pests that could devastate local agriculture, natural forested areas, ecosystems , and also ensuring stable food production and supply.
- Safeguarding Biodiversity: By controlling the import of potentially harmful species, these regulations help protect the biodiversity of local ecosystems.
- Economic Stability:
- Reducing Economic Losses: Preventing pest outbreaks reduces the economic losses that farmers and the agricultural industries might otherwise face.
- Supporting Trade: By maintaining a healthy agricultural environment and a clean phytosanitary status, the country can maintain market access for our major commodities and improve foreign exchange.
- Public Health:
- Safe Food Supply: Ensuring that imported plant products are free from pests contributes to a safe and reliable food supply for consumers.
- Environmental Health: Protecting plants and preventing the entry of invasive species also helps maintain natural ecosystems, clean air, water, and soil, contributing to overall environmental well-being.
- Consumer Confidence:
- Quality Assurance: Knowing that imported plants and plant products meet stringent health standards boosts consumer confidence in the quality and safety of these products.
How the General Public Can Benefit
- Stay Informed:
- Awareness of Regulations: By understanding import conditions, consumers, farmers, agricultural industries and gardeners can make informed choices about the plants and plant products they purchase and import.
- Knowledge of Risks: Awareness of the risks associated with importing plants helps the relevant stakeholders and the public appreciate the importance of these regulations.
- Support Compliance:
- Buy Certified Products: Always opt for plant products that have been legally imported and comply with import conditions and carry the necessary certifications.
- Report Suspicious Items: Notify BAHA authorities if you encounter plant products that do not appear to meet import standards or if you observe any unusual plant health issues.
- Advocate for Strong Policies:
- Promote Plant Health: Support policies and initiatives that strengthen plant health regulations and promote safe trade practices.
- Community Education: Educate others about the importance of import conditions and the role they play in protecting local agriculture and ecosystems.
Export Conditions
Export Certifications: Ensuring Safe and Healthy Plant Trade
Export certification plays a vital role in international trade by ensuring that plants and plant products meet the health standards of importing countries. This process helps prevent the spread of regulated pests, and protecting global agriculture and natural ecosystems. For the productive sector and export logistics services understanding export certifications can provide insights into the importance of plant health in international commerce and the measures taken to maintain it.
What is Export Certifications?
Export certification refers to official procedures carried out by the Plant Health Department of BAHA, which include rigorous inspection and testing of commodities confirming that plants and plant products meet specific phytosanitary requirements as determined by the importing country. The Department issues phytosanitary certificates and other supporting documents that attest to compliance with such conditions. These certifications are crucial for facilitating the smooth and safe cross-border trade of agricultural products.
How Export Certifications Work
- Inspection and Testing:
- Field Inspections: Plants and plant products are inspected in the field or at production sites as well as in packing facilities to ensure they are free from regulated pests.
- Laboratory Testing: Samples may be taken for laboratory analysis to detect any pest infestations that are not visible to the naked eye.
- Compliance with International Standards:
- Phytosanitary Standards: Export certifications ensure compliance with international phytosanitary standards set by organizations such as the International Plant Protection Convention (IPPC).
- Country-Specific Phytosanitary Requirements: Each importing country may have specific plant health requirements, and the inspection and certification process ensures these are met.
- Issuance of Certificates:
- Phytosanitary Certificates: Once plants or plant products pass inspections and tests, a phytosanitary certificate is issued. This document verifies that the shipment complies with the importing country’s phytosanitary regulations
- Treatment Certificates: Some countries require separate treatment certificates for specific commodities other than those stated in the phytosanitary certificate. The department issues these separately..
- Documentation for Trade: These certificates are included in the documentation accompanying the shipment, ensuring transparency and compliance during customs inspections.
Benefits of Export Certifications
- Protecting Global Agriculture:
- Preventing Cross-Border Pest Spread: By ensuring that exported plants are free from regulated pests, export certification helps prevent the spread and introduction of harmful organisms that can devastate crops and natural ecosystems.
- Safeguarding Food Security: Healthy plants contribute to stable agricultural production, supporting food security worldwide.
- Facilitating International Trade:
- Market Access: Export certification enables producers to access international markets, boosting trade opportunities and economic growth.
- Building Trust: Export Certification builds trust between trading partners, ensuring that agricultural products meet the required phytosanitary standards.
- Supporting Local Economies:
- Economic Growth: Access to international markets allows farmers and exporters to expand their businesses, generate foreign exchange and contribute to local and national economic development.
- Job Creation: Increased trade opportunities can lead to job creation in the agricultural and related sectors.
- Consumer Confidence:
- Quality Assurance: For consumers, export certifications provide assurance that imported plant products are healthy and safe, maintaining confidence in the quality of food agricultural planting material and ornamental plants.
How the General Public Can Benefit
- Understanding the Process:
- By learning about export certification, the general public can appreciate the measures taken to ensure the safety and quality of the plants and plant products they consume.
- Supporting Local Agriculture:
- Awareness of export certification can encourage support for local farmers and producers who adhere to high phytosanitary standards, promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
- Making Informed Choices:
- Consumers can make informed choices by opting for products that have been certified, knowing that these products have met stringent phytosanitary standards.
- Advocating for Plant Health:
- Understanding the importance of plant health in global trade can inspire individuals to advocate for robust plant health regulations and practices in their communities and beyond.
Export certification is a key component of safe and healthy international plant trade. This ensures that plants and plant products meet stringent phytosanitary standards, and protecting global agriculture and ecosystems. For the general public, understanding export certifications highlights the importance of plant health and the rigorous processes in place to maintain it. This knowledge not only fosters appreciation for the quality and safety of imported plant products but also encourages support for sustainable agricultural practices and robust plant health regulations.
Surveilance
Pest Surveillance
Pest Surveillance: Protecting Plant Health for a Better Future




Pest surveillance is a proactive approach to safeguarding the health of plants in our agricultural production areas, gardensand natural environments. By regularly monitoring and collecting data, we can detect and address potential issues early, ensuring that our plants stay healthy and productive. This practice benefits everyone, from home gardeners to commercial farmers, by maintaining the beauty and productivity of our green spaces.
What is Pest Surveillance?
Pest Surveillance involves a process whereby information on pests is obtained through specific surveillance and general surveillance, with the objective of detecting regulated pests and other pests of importance in a timely manner to eradicate, suppress, and prevent the further spread of these within a region or throughout the country. in an effort to protect agriculture and natural environments
How Does Pest Surveillance Work?
Specific surveillance is an official process carried out by the Plant Health Department of BAHA alone or in collaboration with industry stakeholders. It includes the following aspects:
- Regular Monitoring:
- Routine Checks: Key industries and production areas are routinely checked by Plant Health Officers for specific pests of quarantine importance. These may include whole fields or sentinel plots in high-risk areas.
- Data Collection:
- Field Notes: Officers keep records and include these in a database for reporting purposes and as proof of the absence of key pests.
- Sample Collection: Plant Health Officers collect suspicious samples of organisms or plant tissue, and submit these to the laboratory for confirmation.
- Use of Technology:
- Specific forms: Field data is generally collected on specific forms designed for the agricultural crop and target pests, which are then submitted for data storage.
- Mobile Apps: Officers also utilize specific apps for recording information for appropriate data storage.
- Remote Tools: For larger areas, drones and satellite imagery can be used to monitor plant health and spot issues from above, followed by ground inspections to verify.
- Documentation:
- Record Keeping: All surveillance data is stored for reporting purposes and for proof that the country is free of certain quarantine pests or to notify of the presence of new pests.
Benefits
- Producers can enjoy market access for their products since the country is maintained free of
quarantine pests. - Government and regulators: specific surveillance provides the basis for quick detection and possible eradication of quarantine pests. On the very least, it is possible to prevent further spread to other production areas
General Surveillance
General Surveillance: Everybody can contribute to Plant Health
General surveillance is an important part of determining the pest status of the country. It involves the casual observation of plants in our surroundings. Unlike specific active surveillance, which involves systematic and scheduled inspections by the plant health authority, general surveillance relies on the National Plant Protection Organization obtaining and verifying information on pests from different sources other than specific surveys. These may include reports made by the public, gardeners, researchers, farmers, technicians, and from academia and scientific publications. This approach empowers individuals to contribute to the health of plants in their production areas, gardens, communities, and natural environments.




How Does General Surveillance Work?
- Casual Observation:
- Gardeners: Keen gardeners observe their plans almost on a daily basis. Oftentimes new pests appear in these settings; as you tend to your garden, casually observe your plants for any signs of distress, such as discoloration, wilting, unusual spots, or insect activity.
- Farmers: Farmers are always concerned with pests and a significant part of management is related to pest management. Farmers know when there is a new pest problem.
- Extension Offices: Extension personnel are more likely to observe pests due to their continuous visits to farms and interactions with farmers. They are also generally aware of the probability of new pest incursions and the importance of these.
- Foresters: Forrest rangers and specialists may detect specific pests in these natural areas. Please report any new observations to the Plant Health department.
- Researchers: agricultural specialists have a tendency to discover new organisms and quickly write scientific articles to publish in journals. Please verify first with the Plant Health Department for clearance. Severe damage can be done to our exporters if our trading partners find out through an unofficial source and halt trade of certain commodities.
- Community Members: When walking through parks, community gardens, or public green spaces, members of the public may note irregularities in plants and may be curious enough to call somebody.
- Reporting:
- Local Authorities: Everybody is encouraged to report any suspicious plant health issues to local agricultural extension services, or directly to the Plant Health Department.
- Education and Awareness:
- Stay Informed: Farmers and gardeners are encouraged to learn about common plant pests in your area so you can recognize symptoms
- Spread the Word: : Everyone is encouraged to educate your family, friends, and neighbors about the importance of observing and reporting plant health issues and likewise to promptly inform of suspicious organisms and symptoms in plants.
Benefits to the General Public
- Community Health:
- Healthy plants contribute to a healthier industries and the environment, providing cleaner air, shade, and aesthetic beauty. Your observations can help maintain these benefits for everyone.
- Early Detection:
- By reporting problems early, you help prevent the spread of pests, protecting not just your plants but those in your community as well.
- Cost Savings:
- Early intervention can save significant costs associated with treatments or replacing diseased plants.
- Educational Value:
- General surveillance offers a learning opportunity for people of all ages. It encourages a deeper understanding and appreciation of plant health and environmental stewardship.
- Community Engagement:
- Engaging in general surveillance fosters a sense of community and shared responsibility for the local environment.
How You Can Get Involved
- Observe Regularly:
- Make it a habit to observe the plants in your farm, garden and community spaces regularly. Simple actions like walking your dog or visiting a park can become opportunities for surveillance.
- Learn and Share:
- Equip yourself with knowledge about common plant health issues. Share your knowledge with others to increase community awareness and participation.
- Report Promptly:
- Don’t hesitate to report any unusual plant symptoms to local authorities or through online platforms. Early reports can make a big difference.
- Join Local Groups:
- Participate in local gardening clubs, community gardens, or environmental groups. These organizations often have systems in place for reporting and addressing plant health issues.
- Use Technology:
- Take advantage of gardening apps to increase your knowledge and to report issues to the Plant Health Department or to the extension services of the Ministry of Agriculture.
Diagnostics
Field Investigation and Diagnostics





Field investigation and diagnostics are critical components of plant health management. These processes involve systematic approaches to identify, monitor, and accurately identify plant pests. Accurate diagnostics and timely intervention can prevent widespread crop damage, ensuring healthy growth and optimal yield.
Steps in Field Investigation
- Preliminary Assessment:
- Visual Inspection: Plant Health officers and specialists conduct an initial visits to identify visible symptoms such as discoloration, wilting, spots, or deformities or the actual presence of pests such as insects and mites.
- Historical Analysis: The officers gather information on previous crop health issues, weather conditions, soil quality, and farming practices.
- Sampling:
- Representative Sampling: The officers collect samples from different parts of the field, including affected and unaffected areas, to ensure comprehensive analysis.
- Sample Handling: The officers properly label and store samples to prevent contamination and degradation and to ensure chain of custody.
- Symptom Documentation:
- Photographic Records: The officers take clear photographs of symptoms, including close-ups and wide-angle shots, to document the extent and nature of the problem.
- Detailed Notes: The officers record observations on the type, severity, and distribution of the organisms, symptoms, as well as environmental conditions and any recent changes in cultivation practices.
Diagnostics Techniques
- Visual Diagnosis:
- Symptom Comparison: The officers compare observed symptoms with known disease profiles from reference guides or online databases
- Expert Consultation: The officers seek advice from plant health specialists such as plant pathologists and entomologists for uncertain cases.
Importance of Accurate Diagnostics
- Targeted Treatment:
- Implementing precise treatments based on accurate diagnostics reduces the unnecessary use of pesticides and fertilizers, promoting sustainable practices.
- Early Intervention:
- Early detection and diagnosis allow for timely intervention for implementing eradication or mitigation to minimize the economic impact of pests on crop yield and quality.
- Informed Decision-Making:
- Accurate diagnostics provide essential data for making informed decisions on crop management, improving overall plant health and productivity.
Field investigation and diagnostics are vital for effective plant health management. By combining visual inspections, laboratory analyses, and advanced technologies, farmers and agronomists can accurately diagnose plant health issues and implement targeted interventions. This comprehensive approach will not only enhances crop productivity but also promotes sustainable agricultural practices, ensuring long-term environmental and economic benefits.
Laboratory Diagnostics





Laboratory diagnostics is a critical support process or making informed decisions and implementing effective pest management strategies. It also provides the Plant Health Department with the necessary basis for declaring the country or areas within the country as free of certain pests a condition creates market access and supports trade. Laboratory diagnosis also supports the import regulatory process by ensuring that regulated pests do not get introduced into the country through imported commodities.
Key Laboratory Diagnostic Techniques
- Microscopic Examination:
- Pest Identification: Microscopy allows for the detailed examination of plant tissues and organisms through the use of stereoscopes and compound microscopes to identify arthropod pests as well as pathogens such as fungi, bacteria, and nematodes.
- Molecular Diagnostics:
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): PCR is a highly sensitive technique used to detect specific DNA or RNA sequences of pathogens. This method allows for the rapid and accurate identification of viruses, bacteria, and fungi, even at low concentrations.
- Serological Tests:
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA): ELISA tests detect the presence of specific proteins or antigens associated with pathogens. This method is widely used for diagnosing viral infections in plants
- Culture Techniques:
- Pathogen Isolation: By culturing samples on selective media, lab technicians can isolate and identify pathogenic bacteria and fungi. This method is useful for confirming the presence of specific pathogens and for further testing their characteristics.
Benefits of Laboratory Diagnostics
- Accuracy and Precision:
- Laboratory diagnostics provide highly accurate and precise results, essential for identifying the exact cause of plant health issues which guide decision-making.
- Early Detection:
- Advanced techniques allow for the early detection of pathogens and nutrient imbalances, enabling timely intervention before problems become widespread.
- Informed Decision-Making:
- Detailed diagnostic information helps the Plant Health Department to initiate appropriate actions or to provide farmers and agronomists with the basis for make informed decisions about treatment strategies, and improving the effectiveness of plant health management.
- Cost-Effective Management:
- By accurately identifying the problem, laboratory diagnostics help avoid unnecessary treatments, reducing costs and minimizing environmental impact.
Publication And Manuals
Trade Facilitation

Medfly Program

Pest Diagnostics

FOC TR4

Contact Us
How can the Plant Health Department help you?
Plant pest is any species, strain or biotype of plant, animal or pathogenic agent injurious to plant or plant products. These may include plant species considered to be weeds, insects, mites and nematodes and pathogens such a fungi, bacteria, phytoplasmas, viruses and viroids.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is a comprehensive approach to controlling pests and diseases that combines biological, cultural, mechanical, and chemical methods.
IPM aims to minimize environmental impact and promote sustainable pest control by using:
Biological Controls: : Natural predators or parasitoids, and entomopathogens
Cultural Practices: Crop rotation, proper planting times and resistant varieties
Mechanical Controls: Traps, barriers, hand-picking pests.
Chemical Controls: Targeted use of pesticides when necessary.
Common signs of nutrient deficiencies include:
Nitrogen: Yellowing of older leaves, stunted growth.
Phosphorus: Dark green or purplish leaves, poor root development.
Potassium: Brown or yellow leaf edges, weak stems.
Calcium: Tip burn on young leaves, blossom end rot in fruits.
A plant health diagnostic lab helps identify plant pests, and through various proven technicques such as microspcopy, molecular biology, microbiology and serology.
You can contribute by:
Reporting Issues: Inform BAHA or Ministry of Agricultural about unusual plant symptoms or pest outbreaks.
Practicing Good Hygiene: Clean tools and equipment to prevent the spread of diseases.
Educating Yourself: Learn about common plant health issues and best practices for prevention and control.
Supporting Research: Participate in citizen science projects and support organizations focused on plant health research and education.

